IDEXX point-of-care diagnostics
Powerful on their own. Unstoppable together.
IDEXX in-house veterinary analysers work together to give you actionable insights while your patient is in the practice.

Meet the new additions to your team
Our point-of-care analysers were built to support each other, work quickly, and communicate seamlessly—like an extension of your team. Together, they can make a big difference in your day-to-day, helping your practice operate more efficiently and providing you and your staff with advanced technology, tools, and experts to help you interpret results and determine next steps.

Catalyst One Chemistry Analyser
Get accurate, comprehensive results in as little as 8 minutes—all in one run.

ProCyte One Haematology Analyser
The fast, effortless way to get an accurate CBC in-house.

ProCyte Dx Haematology Analyser
The supercharged haematology analyser that dives even deeper.

SediVue Dx Urine Sediment Analyser
The connected, low-touch way to get to confident clinical decisions faster.

IDEXX inVue Dx Cellular Analyser
Diagnose and act on clinically important cell types with reference laboratory-level accuracy, in real time, with a slide-free workflow.

The complete suite
A team of connected analysers that help your practice run smoothly.
Part lab. Part lab partner.
The in-house lab that always has your back.
Keep your day on track.
By being low touch, fully connected, and able to produce actionable results quickly during the patient visit, we help your practice run smoothly in moments that would otherwise slow you down.
Wave goodbye to manual entry.
Too much time, effort, and headaches are wasted punching in patient info. A connected lab means less repetitive manual entry, missed charges, and opportunity for error.
A platform. Not just a suite.
Our analysers are fully capable out of the box, but their value increases over time with automatic software upgrades, introduction of new tests, and ongoing enhancements.
You’re never on your own.
Results are provided clearly and within an ecosystem of support. This includes everything from helpful technology (suggested next steps, interpretive aids, and IDEXX SmartService Solutions) to people (Field Service Representatives and live consults).

The secret to any great team? Communication.
Connecting everything to help you get answers, see clearly, and act accordingly.
Working together seamlessly is no accident. It’s the result of strong connections. The IDEXX VetLab Station is fully supported by IDEXX SmartService Solutions and acts as the point person—connecting your diagnostics to your PIMS, VetConnect PLUS, and the cloud. Together, all these connections, access, and shared functionality help your practice run more smoothy and ensure your patient records are complete.
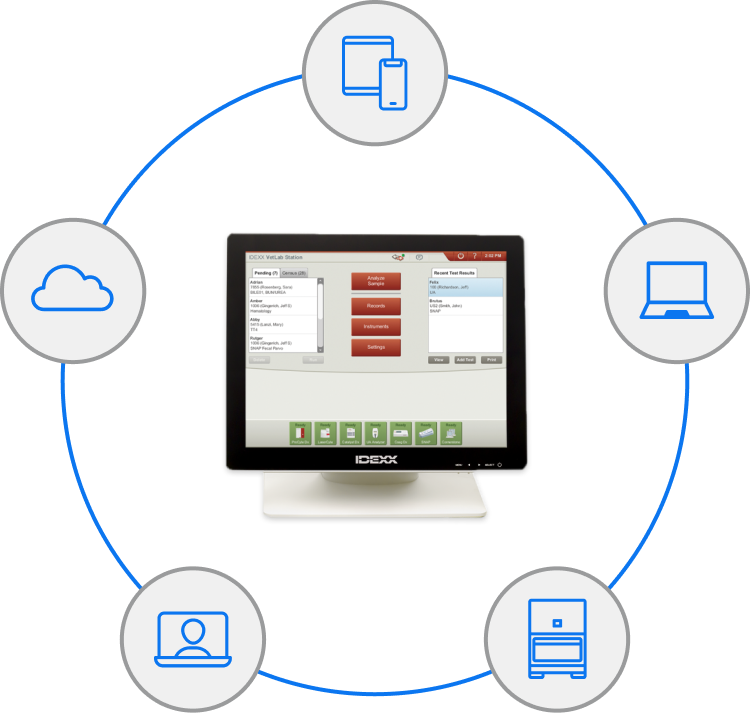
IDEXX VetLab Station
Connection to your IDEXX point-of-care analysers starts with the IDEXX VetLab Station, which is the command center for running and queuing your analysers.
It also acts as the bridge between your in-house lab and your PIMS, eliminating double data entry and making sure charges are captured.
IDEXX SmartService Solutions
It helps you save time and improve analyser performance with:
+ Seamless software updates, providing the latest features and enhancements.
+ Proactive system updates to optimize analyser performance.
+ Full data storage and backup.
+ Real-time, 24/7 access to customer support.
PIMS
PIMS integration means you’ll never miss a charge and your staff will spend less time on repetitive manual entry. IDEXX Software Solutions come with full integration but contact your PIMS provider to check on their status.
VetConnect PLUS
VetConnect PLUS gives you real-time order status for every patient on any device. You can also share diagnostic results and personalised, client-friendly result summaries with a click (or a tap).
You work best when your lab just works.
When it comes to workflow and efficiency, your in-house lab can make a big difference. Learn how in our latest guide to evaluating in-house analysers.
Upgrade your lab. No up-front cost.
Ready for a more complete view of your patient’s care? Sign up for IDEXX 360 and your practice will get the latest equipment with no up-front cost.
+ No capital investment or lease required
+ No maintenance fees for analysers
+ Worry-free first-year commitment
Ready for a quick huddle?
Fill out the form to discuss these important questions with your Veterinary Diagnostic Consultant.
How do you and your practice keep up with new tests and trends in veterinary medicine?
How does reliable support (or lack of it) affect your team?
What part of your diagnostic workflow slows you down the most?